Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes contains – Edition = 7th, Pages chapters (1-92) = 221, Pages Pyq = 14, Format = Pdf. Buy All in One combo and Get More Discount & Benefits = Click Here
|| Content of Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes ||
- Chapter: 1 – Historical Background
- Chapter: 2 – Making of the Indian Constitution
- Chapter: 3 – Concept of the Constitution
- Chapter: 4 – Feature of the Constitution
- Chapter: 5 – Preamble of the Constitution
- Chapter: 6 – Union and its Territory
- Chapter: 7 – Citizenship
- Chapter: 8 – Fundamental Rights
- Chapter: 9 – Directive Principles of our State Policy
- Chapter: 10 – Fundamental Duties
- Chapter: 11 – Amendment of the Constitution
- Chapter: 12 – Basic Structure of the Constitution
- Chapter: 13 – Parliamentary System
- Chapter: 14 – Federal System
- Chapter: 15 – Centre–State Relations
- Chapter: 16 – Inter State Relations
- Chapter: 17 – Emergency Provisions
- Chapter: 18 – President
- Chapter: 19 – Vice-President
- Chapter: 20 – Prime Minister
- Chapter: 21 – Central Council of Ministers
- Chapter: 22 – Cabinet Committee
- Chapter: 23 – Parliament
- Chapter: 24 – Parliamentary Committees
- Chapter: 25 – Indian Parliamentary Group
- Chapter: 26 – Supreme Court
- Chapter: 27 – Judicial Review
- Chapter: 28 – Judicial Activism
- Chapter: 29 – Public Interest Litigation
- Chapter: 30 – Governor
- Chapter: 31 – Chief Minister
- Chapter: 32 – State Council Of Ministers
- Chapter: 33 – State Legislature
- Chapter: 34 – High Court
- Chapter: 35 – Subordinate Courts
- Chapter: 36 – Tribunals
- Chapter: 37 – Consumer Commissions
- Chapter: 38 – Lok Adalats and Other Courts
- Chapter: 39 – Panchayati Raj
- Chapter: 40 – Municipalities
- Chapter: 41 – Union Territories
- Chapter: 42 – Scheduled and Tribal Areas
- Chapter: 43 – Election Commission
- Chapter: 44 – Union Public Service Commission
- Chapter: 45 – State Public Service Commission
- Chapter: 46 – Finance Commission
- Chapter: 47 – Goods and Services Tax Council
- Chapter: 48 – National Commission For SCs
- Chapter: 49 – National Commission For STs
- Chapter: 50 – National Commission For BCs
- Chapter: 51 – Special Officer For Linguistic Minorities
- Chapter: 52 – Comptroller and Auditor General of India
- Chapter: 53 – Attorney General of India
- Chapter: 54 – Advocate General of The State
- Chapter: 55 – Constitutional Prescriptions
- Chapter: 56 – Niti Aayog
- Chapter: 57 – National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- Chapter: 58 – State Human Rights Commission
- Chapter: 59 – National Commission for Women
- Chapter: 60 – National Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- Chapter: 61 – National Commission for Minorities
- Chapter: 62 – Central Information Commission
- Chapter: 63 – State Information Commission
- Chapter: 64 – Central Vigilance Commission
- Chapter: 65 – Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- Chapter: 66 – Lokpal and Lokayuktas
- Chapter: 67 – National Investigation Agency
- Chapter: 68 – National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- Chapter: 69 – Bar Council of India
- Chapter: 70 – Law Commission of India
- Chapter: 71 – Delimitation Commission of India
- Chapter: 72 – Co-Operative Societies
- Chapter: 73 – Official Language
- Chapter: 74 – Public Services
- Chapter: 75 – Rights And Liabilities of the Government
- Chapter: 76 – Special Provisions Relating to Certain Classes
- Chapter: 77 – Special Provisions for Some States
- Chapter: 78 – Political Parties
- Chapter: 79 – Role of Regional Parties
- Chapter: 80 – Elections
- Chapter: 81 – Election Laws
- Chapter: 82 – Electoral Reforms
- Chapter: 83 – Voting Behaviour
- Chapter: 84 – Coalition Government
- Chapter: 85 – Anti-Defection Law
- Chapter: 86 – Pressure Groups
- Chapter: 87 – National Integration
- Chapter: 88 – Foreign Policy
- Chapter: 89 – National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution
- Chapter: 90 – Landmark Judgements and their Impact
- Chapter: 91 – Important Doctrines of Constitutional Interpretation
- Chapter: 92 – World Constitutions
- Prelims Previous Year Paper
- Mains Previous Year Paper
|| Brief Introduction of Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes ||
Chapter: 1 – Historical Background
- The Company Rule (1773-1858)
- The Crown Rule (1858-1947)
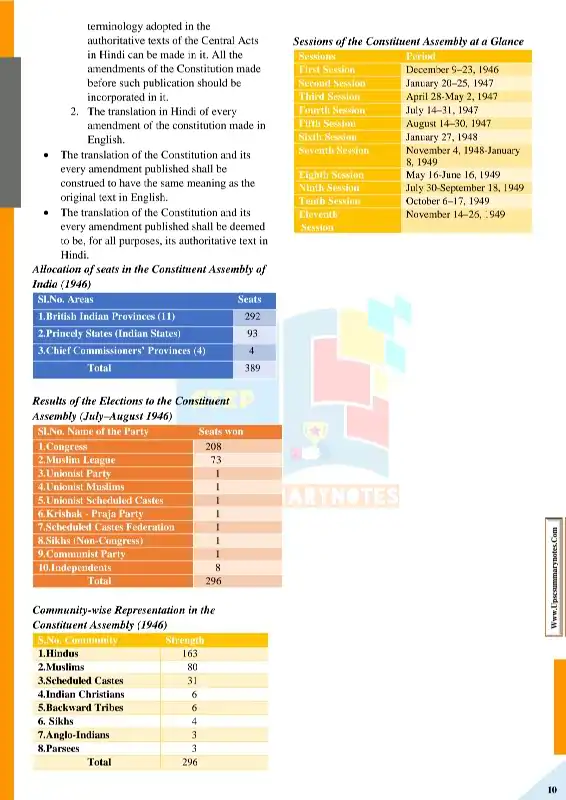
Chapter: 2 – Making of the Indian Constitution
- Committees of the Constituent Assembly
- Enforcement of the Constitution
- Experts Committee of the Congress
- Criticism of the Constituent Assembly
- Hindi Text of the Constitution
Chapter: 3 – Concept of the Constitution
- Meaning
- Functions
- Qualities
- Classification
- Constitutionalism and Constitutional Government
Chapter: 4 – Feature of the Constitution
- Salient Features of the Constitution
- Criticism of the Constitution
- Various Sources of The Indian Constitution
Chapter: 5 – Preamble of the Constitution
- Text of the Preamble
- Key Words in the Preamble
- Preamble as Part of the Constitution
- Amenability of the Preamble
Chapter: 6 – Union and Its Territory
- Union of State
- Parliament’s Power to Reorganise the State
- Exchange of Territories with Bangladesh
- Evolution of States and Union Territories
Chapter: 7 – Citizenship
- Constitutional Provision
- Citizenship Act, 1955
- Loss of Citizenship
- Single Citizenship
- Overseas Citizenship of India
Chapter: 8 – Fundamental Rights
- Definition of State
- Laws Inconsistent with Fundamental Rights
- Right To Equality (14-18)
- Right To Freedom
- Right Against Exploitation
- Right To Freedom of Religion
- Cultural and Educational Rights
- Right To Constitutional Remedies
- Writs—Types and Scope
- Armed Forces and Fundamental Rights
- Martial Law and Fundamental Rights
- Effecting Fundamental Rights
- Exceptions to Fundamental Rights
- Criticism of Fundamental Rights
- Significance of Fundamental Rights
Chapter: 9 – Directive Principles of our State Policy: Part IV (Articles 36-51)
- Features of the Directive Principles
- Classified into Three Categories
- New Directive Principles
Chapter: 10 – Fundamental Duties
- Swaran Singh Committee Recommendations
- List of Fundamental Duties
- Characteristics
- Significance
- Criticism of FDs
- Verma Committee Observations
Chapter: 11 – Amendment of the Constitution
- Types Of Amendments In the Indian Constitution
- Procedure For Amendment
- Criticism Of Amendment Procedure
Chapter: 12 – Basic Structure of the Constitution
- The emergence of the Basic Structure
- Elements of the Basic Structure
Chapter: 13 – Parliamentary System
- Features of Parliamentary Government
- Features of Presidential Government
- Merits of the Parliamentary System
- Demerits of the Parliamentary System
- Reasons for Adopting Parliamentary System
- The distinction between Indian and British Models
Chapter: 14 – Federal System
- Federal Features of the Indian Union
- Unitary
- Federal Features of the Constitution
- Issues and Challenges Faced by Indian Federalism
Chapter: 15 – Centre-State Relations
- Legislative Relations
- Administrative Relations
- Financial Relations
- Trends in Centre-State Relations
Chapter: 16 – Inter-State Relations
- Inter-State Water Disputes
- Inter-State Councils
- Inter-State Trade and Commerce
- Zonal Councils
Chapter: 17 – Emergency Provisions
- 352 – National Emergency
- 356 – President’s Rule
- 360 – Financial Emergency (Never Imposed Till Date)
- Criticism of the Emergency Provisions
Chapter: 18 – President
- Election of the President
- Qualification, Oath and Condition
- Term, Impeachment and Vacancy
- Powers and Functions of the President
- Veto Power
- Ordinance-Making Power
- Pardoning Power of the President
Chapter: 19 – Vice-President
- Election
- Qualifications
- Powers and Functions
- Compared
Chapter: 20 – Prime Minister
- Appointment of the Prime Minister
- Powers and Functions of the Pm
- Relationship With the President
- Cm Who Became Prime Ministers
Chapter: 21 – Central Council of Ministers
- Constitutional Provisions
- Nature of Advice by Ministers
- Appointment of Ministers
- Responsibility of Ministers
- Composition of The Council of Ministers
- Composition of The Council of Minister
- Role of Cabinet
- Kitchen Cabinet
Chapter: 22 – Cabinet Committee
- Features of Cabinet Committees
- Functions of Cabinet Committees
- List of Cabinet Committees
Chapter: 23 – Parliament
- Organisation of Parliament
- Composition
- Duration
- Membership of Parliament
- Presiding Officers of Parliament
- Sessions of Parliament
- Devices of Parliamentary Proceedings
- Legislative Procedure in Parliament
- Joint Sitting of Parliament
- Budget in Parliament
- Multifunctional Role of Parliament
- Position of Rajya Sabha
Chapter: 24 – Parliamentary Committees
- Classification
- Financial Committees
- Committees to Inquire
- Committees to Scrutinise
- Committees Relating to the Day-to-Day Business of the House
Chapter: 25 – Indian Parliamentary Group
- Composition of the e Group
- Objectives of the Group
- Functions of the Group
- The Group and IPU
- The Group and CPA
Chapter: 26 – Supreme Court
- Composition and Appointment
- Qualifications, Oath, Tenure, Removal of Judges
- Tenure and Removal
- Acting, Ad Hoc, Retired Judges
- Procedure of Court
- Independence of Supreme Court
- Jurisdiction and Powers of the Supreme Court
Chapter: 27 – Judicial Review
- Meaning
- Importance of Judicial Review
- Constitutional Provisions for Judicial Review
- Scope of Judicial Review
- Judicial Review of Ninth Schedule
Chapter: 28 – Judicial Activism
- Meaning of Judicial Activism
- Judicial Review and Judicial Activism
- Justification of Judicial Activism
- Activators of Judicial Activism
- Apprehensions of Judicial Activism
- Judicial Activism Vs. Judicial Restraint
Chapter: 29 – Public Interest Litigation
- Meaning of PIL
- Features of PIL
- Scope of PIL
- Principles of PIL
- Guidelines for Admitting of PIL
Chapter: 30 – Governor
- Appointment of Governor
- Conditions of the Governor’s Office
- Powers and Functions of Governor
- Constitutional Position of Governor
Chapter: 31 – Chief Minister
- Appointment Of Chief Minister
- Powers And Functions Of Cm
- Relationship With the Governor
Chapter: 32 – State Council of Ministers
- Constitutional Provisions
- Nature of Advice by Ministers
- Appointment of Ministers
- Responsibility of Ministers
- Cabinet
Chapter: 33 – State Legislature
- The organisation of the State Legislature
- Composition of Two Houses
- Duration of Two Houses
- Membership of the State Legislature
- Presiding Officers of State Legislature
- Sessions of State Legislature
- Legislative Procedure in State Legislature
- Position of Legislative Council
Chapter: 34 – High Court
- Composition and Appointment
- Qualifications, Oath, Salaries
- Tenure, Removal and Transfer
- Acting, Additional and Retired Judges
- Independence of the High Court
- Jurisdiction and Powers of the High Court
Chapter: 35 – Subordinate Courts
- Constitutional Provisions
- Structure and Jurisdiction
- Lok Adalats
- Permanent Lok Adalats
- Family Courts
- Gram Nyayalayas
Chapter: 36 – Tribunals
- Administrative Tribunals
- Tribunals for other Matters
Chapter: 37 – Consumer Commission
- National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
- State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
- District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
Chapter: 38 – Lok Adalats and other Courts
- Lok Adalats
- Permanent Lok Adalats
- Family Courts
- Gram Nyayalayas
- Commercial Courts
Chapter: 39 – Panchayati Raj
- Evolution of Panchayati Raj
- 73rd Amendments Act of 1992
- Compulsory and Voluntary Provisions
- Pesa Act of 1996 (Extension Act)
- Reasons for Ineffective Performance
Chapter: 40- Municipalities
- Evolution of Urban Bodies
- 74th Amendment Act Of 1992
- Types of Urban Governments
- Municipal Personnel
- Municipal Revenue
- Central Council Of Local Government
Chapter: 41 – Union Territories
- Creation of Union Territories
- Administration of Union Territories
- Special Provisions for Delhi
- Advisory Committees of Union Territories
Chapter: 42 – Scheduled and Tribal Areas
- Administration of Scheduled Areas
- Administration of Tribal Areas
Chapter: 43 – Election Commission
- Composition
- Powers and Functions
- Vision, Mission and Principles
Chapter: 44 – Union Public Service Commission
- Composition
- Removal
- Functions
- Limitations
- Role
Chapter: 45 – State Public Service Commission
- Composition
- Removal
- Functions
- Limitations
- Role
- Joint State Public Service Commission
Chapter: 46 – Finance Commission
- Composition
- Functions
- Advisory Role
Chapter: 47 – Goods and Services Tax Council
- Establishment of The Council
- Vision and Mission of the Council
- Composition of the Council
- Working of the Council
- Functions of the Council
Chapter: 48 – National Commission for SCs
- Evolution of the Commission
- Functions of the Commission
- Report of the Commission
- Powers of the Commission
Chapter: 49 – National Commission for STs
- Separate Commission for STs
- Functions of the Commission
- Other Functions of the Commission
- Report of the Commission
- Powers of the Commission
Chapter: 50 – National Commission for BCs
- Establishment of the Commission
- Functions of the Commission
- Report of the Commission
- Powers of the Commission
Chapter: 51 – Special Officer for Linguistic Minorities
- Constitutional Provisions
- Vision and Mission
- Functions and Objectives
Chapter: 52 – Comptroller and Auditor General of India
- Appointment and Term
- Independence
- Duties and Powers
- Role
- Cag and Corporations
- Appleby’s Criticism
Chapter: 53 – Attorney General of India
- Appointment and Term
- Duties and Functions
- Rights and Limitations
- Solicitor General of India
Chapter: 54 – Advocate General of the State
- Appointment and Term
- Duties and Functions
Chapter: 55 – Constitutional Prescriptions
- Compositions
- Appointments
- Age
- Oaths
- Term
- Salaries
- Resignations
- Removals and Dissolutions
- Submission of Reports
Chapter: 56 – Niti Aayog
- Establishment
- Composition
- Specialised Wings
- Objectives
- Functions
- Guiding Principles
- Cooperative Federalism
- Criticism
- Attached Offices
Chapter: 57 – National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- Establishment of the Commission
- Functions and Powers of NHRC
- Composition of the Commission
- Working of the Commission
- Role of the Commission
Chapter: 58 – State Human Rights Commission
- Composition
- Functions of the Commission
- Working of the Commission
- 2019 Amendment Act
Chapter: 59 – National Commission for Women
- Establishment
- Composition
- Functions
- Powers
- Working
- Parivarik Mahila Lok Adalat
Chapter: 60 – National Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- Establishment
- Composition
- Functions
- Powers
- Working
- Functions Under Other Acts
- State Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- Children’s Courts
Chapter: 61 – National Commission for Minorities
- Establishment
- Composition
- Functions
- Powers
- Report
Chapter: 62 – Central Information Commission
- Composition
- Tenure and Service Conditions
- Powers and Functions
Chapter: 63 – State Information Commission
- Composition
- Tenure and Service Conditions
- Powers and Functions
- RTI Amendment Act, 2019
Chapter: 64 – Central Vigilance Commission
- Establishment
- Composition
- Organisation
- Functions
- Working
- The Whistleblowers Protection Act, 2014
Chapter: 65 – Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- Establishment of CBI
- Motto, Mission And Vision of CBI
- Organisation of CBI
- Composition of CBI
- Functions of CBI
- Provision of Prior Permission
- CBI Vs. State Police
- CBI Academy
Chapter: 66 – Lokpal and Lokayukta
- Lokpal
- Lokpal and Lokayukta Act 2013
- Lokayuktas
Chapter: 67 – National Investigation Agency
- Establishment of the NIA
- Functions of the NIA
- A vision of the NIA
- The mission of the NIA
- Jurisdiction of the NIA
- Nia (Amendment) Act, 2019
Chapter: 68 – National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- Establishment of the NDMA
- Objectives of the NDMA
- Functions of the NDMA
- Additional Functions of the NDMA
- State Disaster Management Authority
- District Disaster Management Authority
Chapter: 69 – Bar Council of India
- Establishment
- Composition
- Functions
- State Bar Councils
- Types of Advocates
Chapter: 70 – Law Commission of India
- Historical Background
- Commissions Constituted so Far
- Composition
- Functions
- Working
- Role
Chapter: 70 – Delimitation Commission of India
- Rationale of Delimitation
- Commissions Established so Far
- Constitutional Provisions
- Fourth Delimitation Commission
- Implementation of the Recommendations
- Delimitation Commission (2020)
- Delimitation In J&K
- Order of the Commission
- Recommendations of the Commission
Chapter: 72- Co-Operative Societies
- Constitutional Provisions
- Reasons for the 97th Amendment
Chapter: 73- Official Language
- Language of the Union
- Regional Languages
- Development of the Hindi Language
- Committee of Parliament on Official Language
- Classical Language Status
Chapter: 74 – Public Services
- Classification of Services
- Constitutional Provisions
Chapter: 75 – Rights and Liabilities of the Government
- Property of the Union and the States
- Suits by or Against the Government
- Suits Against Public Officials
Chapter: 76 – Special Provisions Relating to Certain Classes
- The rationale of Special Provisions
- Specification of Classes
- Components of Special Provisions
Chapter: 77 – Special Provisions for Some State
- Provisions for Maharashtra and Gujarat
- Provisions for Nagaland
- Provisions for Assam and Manipur
- Provisions for Andhra Pradesh or Telangana
- Provisions for Sikkim
- Provisions for Mizoram
- Provisions for Arunachal Pradesh and Goa
- Provisions for Karnataka
Chapter: 78 – Political Parties
- Meaning and Types
- Party System in India
- Recognition of a National Party and State Parties
- Rise of Regional Parties in India
Chapter: 79 – Role of Regional Parties
- Features of Regional Parties
- Classification of Regional Parties
- Rise of Regional Parties
- Roles of Regional Parties
- Dysfunctions of Regional Parties
Chapter: 80 – Elections
- Electoral System
- Election Machinery
- Election Process
Chapter: 81 – Election Laws
- Representation of the People Act, 1950
- Representation of the People Act, 1951
- Delimitation Act, 2002
- Other Acts Relating to Elections
- Rules Relating to Elections
Chapter: 82 – Electoral Reforms
- Committees Related to Electoral Reforms
- Electoral Reforms Before 1996
- Electoral Reforms of 1996
- Electoral Reforms after 1996
- Electoral Reforms since 2010
Chapter: 83 – Voting Behaviour
- Meaning of Voting Behaviour
- Significance of Voting Behaviour
- Determinants of Voting Behaviour
- Role of Media in Elections and Voting Behaviour
Chapter: 84 – Coalition Government
- Meaning of Coalition Government
- Features of Coalition Government
- Formation of Coalition Governments
- Merits of Coalition Government
- Demerits of Coalition Government
Chapter: 85 – Anti-Defection Law
- Provisions of the Act
- Evaluation of the Act
- 91st Amendment Act (2003)
Chapter: 86 – Pressure Groups
- Meaning and Techniques
- Pressure Groups in India
- Functions
Chapter: 87 – National Integration
- Meaning of National Integration
- Obstacles to National Integration
- National Integration Council
- National Foundation for Communal Harmony
Chapter: 88 – Foreign Policy
- Principles of Indian Foreign Policy
- Objectives of Indian Foreign Policy
- Gujral Doctrine of India
- Nuclear Doctrine of India
- Connect Central Asia Policy of India
- Act East Policy of India
Chapter: 89 – National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution
- Terms Of Reference Of the Commission
- Nifty Years of Working on the Constitution
- Areas Of Concern: Commission’s Perception
- Recommendations of the Commission
- Earlier Efforts to Review the Constitution
Chapter: 90 – Landmark Judgements and their Impact
- Romesh Thappar Case (1950)
- K. Gopalan Case (1950)
- Champakam Dorairajan Case (1951)
- Shankari Prasad Case (1951)
- Berubari Union Case (1960)
- M. Nanavati Case (1961)
- C. Golak Nath Case (1967)
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973)
- Indira Nehru Gandhi Case (1975)
- D.M. Jabalpur Case (1976)
- Maneka Gandhi Case (1978)
- Bachan Singh Case (1980)
- Minerva Mills Case (1980)
- Waman Rao Case (1980)
- Shah Bano Case (1985)
- C. Wadhwa Case (1986)
- C. Mehta Case (1986)
- Kihoto Hollohan Case (1992)
- Indra Sawhney Case (1992)
- Mohini Jain Case (1992)
- Unni Krishnan Case (1993)
- Supreme Court Advocates-On-Record Association Case (1993)
- R. Bommai Case (1994)
- Vishaka Case (1997)
- Vineet Narain Case (1997)
- Association For Democratic Reforms Case (2002)
- M.A. Pai Foundation Case (2002)
- Naveen Jindal Case (2004)
- Prakash Singh Case (2006)
- Nagaraj Case (2006)
- Coelho Case (2007)
- Aruna Ramachandra Shanbaug Case (2011)
- People’s Union For Civil Liberties Case (2013)
- Lily Thomas Case (2013)
- S.R. Subramanian Case (2013)
- National Legal Services Authority Case (2014)
- Shreya Singhal Case (2015)
- Supreme Court Advocates- On-Record Association Case (2015)
- Shayara Bano Case (2017)
- S. Puttaswamy Case (2017)
- Indian Young Lawyers Association Case (2018)
- Joseph Shine Case (2018)
- Navtej Singh Johar Case (2018)
- Siddiq Case (2019)
- Anuradha Bhasin Case (2020)
- Rambabu Singh Thakur Case (2020)
- Internet And Mobile Association of India Case (2020)
Chapter: 91 – Important Doctrines of Constitutional Interpretation
- Doctrine of Severability
- Doctrine of Waiver
- Doctrine of Eclipse
- Doctrine of Territorial Nexus
- Doctrine of Pith and Substance
- Doctrine of Colourable Legislation
- Doctrine of Implied Powers
- Doctrine of Incidental and Ancillary Powers
- Doctrine of Precendent
- Doctrine of Occupied Field
- Doctrine of Prospective Overruling
- Doctrine of Harmonious Construction
- Doctrine of Liberal Interpretation
Chapter: 92 – World Constitutions
- American Constitution
- British Constitution
- French Constitution
- Japanese Constitution
- Soviet Constitution
- Russian Constitution
- Chinese Constitution
- Swiss Constitution
|| Content of Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Book||
“Indian Polity” by M. Laxmikanth is a comprehensive book that serves as a guide to the Indian political system and governance. It’s a popular reference book for aspirants preparing for various competitive examinations in India, particularly the Civil Services Examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC).
The Laxmikant Polity 7th Edition Pdf in english covers various aspects of Indian polity and governance, including the Constitution of India, fundamental rights, directive principles of state policy, the structure and functions of the government, parliamentary system, federalism, local government, and more. It’s known for its detailed explanations, lucid language, and extensive coverage of topics relevant for competitive exams.
Many candidates find this book helpful not only for learing the basic concepts but also for understanding the nuances of Indian politics and governance, which is crucial for cracking exams like the UPSC Civil Services Examination.
Laxmikant Polity 7th edition Pdf Notes chapters have been thoroughly revised as per the recent developments with an addition of 12 new chapters in this latest edition.
|| T0 Buy Mains Notes Combo Offer ||
- Art and Culture Nitin Singhania Notes
- GC Leong | Certificate Physical and Human Geography Notes
- Environment Shankar Ias Notes
- Ethics Lexicon Notes
- Indian Polity M.Laxmikanth Notes
- Indian Society Topic Wise Notes
- Internal Security Ashok Kumar IPS Notes
- Modern History Spectrum Notes
- Science and Tech Ravi P Agrahari Notes
To Buy Mains Notes Combo – Click Here
|| T0 Buy All In One Combo Offer Notes ||
- For Year = 2024
- Formats = Pdfs
- Language = English
- Get extra 10% off, use code – Allinone10
- Ncert Notes = An Introduction to Indian Art | Ancient History Tamilnadu Board | Ancient India Old Ncert | Economy Ncert (9-12) | Geography Ncert Class (6-12) | Medieval History Tamilnadu Board | Medieval History Old Ncert | Modern History Old Ncert | Political Science Ncert Class (6-12) | Science Ncert class (6-12) | History Ncert class (6-12) | The Story of Civilization Ncert by Arjun Dev | Sociology Ncert class (11-12) |.
- Mains Notes = Art and Culture Nitin Singhania | GC Leong Latest Edition | Environment Shankar Ias | Ethics Lexicon | Indian Polity M.Laxmikanth | Indian Society Topic Wise |Internal Security Ashok Kumar IPS | Modern History Spectrum | Science and Tech Ravi P Agrahari | Indian Economy Ramesh Singh |.
- Ghatna Chakra Prelims Pointer = Environment | General Science | Geography | History | Indian Polity & Governance |Economy |.
- Extra Addon = 2nd ARC Reports Notes | How To Plan Your Study | How to Top UPSC: Strategies for Effective Preparation | Quotation Book | Ultimate Guide to Master Answer Writing: Techniques for Brilliance | UPSC Syllabus and How to Cover it Efficiently |.
- Ncert Edition = 2023-24
- Pointer Edition = 2023
- Give BoostUP in Your = UPSC and State PCS Preparation
- Get free updated notes under = 1 Year
- How to Buy/Download Notes – Click Here
- How to get the Updated Notes – Click Here
![Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes 7th Edition 2024 [PDF] Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes 7th Edition 2024 [PDF]](https://upscsummarynotes.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/0-21.webp)
![1 Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes 7th Edition 2024 [PDF]](https://upscsummarynotes.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/1-10.webp)
![2 Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes 7th Edition 2024 [PDF]](https://upscsummarynotes.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/2-10.webp)







![96 Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes 7th Edition 2024 [PDF]](https://upscsummarynotes.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/96.webp)
![97 Indian Polity M. Laxmikanth Notes 7th Edition 2024 [PDF]](https://upscsummarynotes.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/97.webp)





















Vandana Verma –
Too good to revise at a faster pace.
Nisha Debnath –
One of the best source for upsc aspirants.